Introduction
The process of planning and moving to digital telecare is likely to take some time to complete. Given that customers' digital telephone line migrations have already commenced, the switchover will impact an organisation's existing analogue telecare service before a fully digital telecare service can be put in place. For this reason the checklist is split into two separate, but related, streams that should be completed in parallel:
- Existing services – risk mitigation: this stream of work comprises the tasks that organisations should complete in the short term to understand and mitigate the impact of the digital shift on their existing analogue telecare service and service users.
- Future services – moving to digital telecare: these tasks help organisations to plan and complete their move to digital telecare services.
This report presents the initial tasks organisations should complete. It is likely that these tasks will highlight further work that organisations will need to include in their planning.
An overview of each of the initial tasks is provided as well as links to additional information available to support organisations.
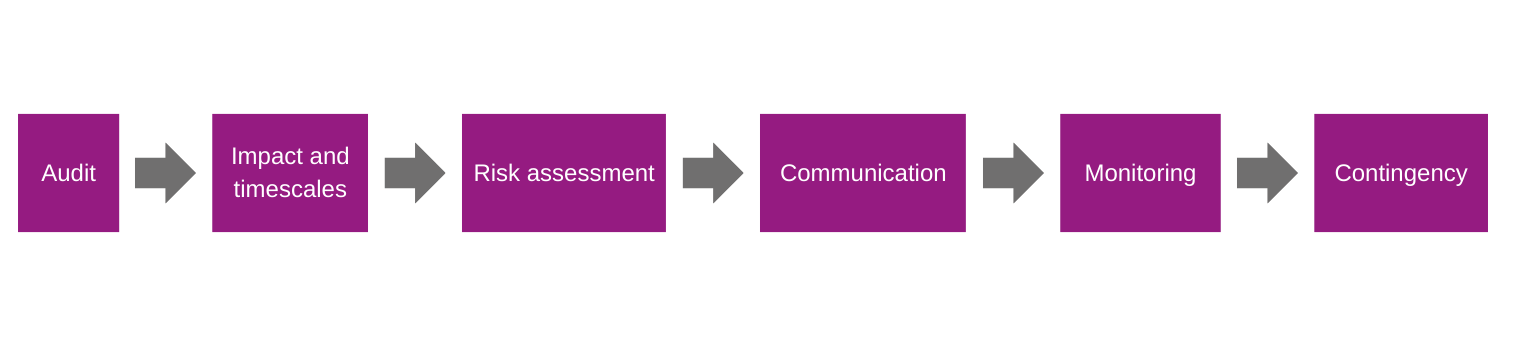
Existing services: risk mitigation
Audit
Understand the existing service
Organisations need to have accurate and current data on the scope of their existing services to allow the impact of the digital switchover to be established and to support their planning for the move to digital telecare.
- Do you have up to date and accurate records on your service users?
- Do you know what alarm equipment and peripherals are currently deployed to each service user?
- Do you understand what other equipment and services that are in use which connect to a telephone line? Examples could include: telehealth devices, activities of daily living, assistive technology, alarm panels, lift lines, building management systems, monitoring equipment, etc.
- Do you know who are the stakeholders associated with telecare services that need to be engaged as part of the response to the digital shift? Examples include: equipment and service suppliers, service users, internal stakeholders, partner agencies/organisations.
Further information:
Department of Digital, Culture, Media & Sport: UK transition from analogue to digital landlines
Impact and timescales
When is the switchover happening and how will existing services be impacted?
Organisations need to establish the impact the digital switchover is likely to have on their existing telecare services and technology. Information from communication providers (telephone companies) should also be collected to understand when these telephony changes may happen.
Collate information from telephone providers about where and when analogue to digital migrations are happening:
- Information is already available from Openreach and Virgin Media.
- Other telephone providers are likely to start providing further detail on their migration plans shortly.
Understand how reliably your current analogue alarm equipment and alarm signalling protocols are likely to operate when connected to a digital telephone line:
- Information can be obtained from suppliers, the TEC Services Association (TSA), and other telecare providers that have completed testing.
- Organisations should include any analogue GSM alarms they use in the scope of information collected.
Understand the likely impact of the digital switchover on the Alarm Receiving Centre (ARC):
- Does the ARC use Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) and/or analogue exchange lines?
- How reliably will the ARC receive analogue telecare calls? How long is this analogue capability likely to remain (impact of the removal of an ARC's ISDN/analogue lines)?
- Can the ARC receive telecare calls using digital signalling protocols? If not, when is this likely to be available?
- Information can be obtained from suppliers, the TSA, and other telecare providers that have completed testing.
Further information:
Openreach: Stop sell exchange list
Virgin Media: Virgin Phone Switchover
BT: What is Digital Voice and How Can I Get it?
Sky: What You Need to Know About Internet Calls
FarrPoint: Analogue Switch off Maps
TSA: The Urgent Need to Test Analogue Devices on Digital Lines
Risk assessment
Organisations need to establish the level of risk to their service users based on their care needs and technology.
Assess the level of risk to each service user. This could include consideration of:
- a service user's care needs, vulnerability, availability of wider support
- the reliability of their existing telecare equipment if it is connected to a digital phone line
- timescales for the migration of their telephone service.
Use the assessed risk and timescales to establish those service users that need additional risk reduction measures to be put in place and/or be prioritised for the rollout of equipment/service upgrades.
Communication
What do service users need to know and when do they contact their telecare provider?
Organisations need to establish what their service users need to be told about the digital switchover. How and when should information be sent? What is the best way to communicate information about a complex technology shift?
Determine the communications that should be sent to service users. This could include:
- initial communication about the digital switchover, its potential impact on telecare services and warnings about the potential for scams
- further communication once a provider has clearer plans and timescales for providing a digital telecare service.
Determine when and how service users should be asked to contact their provider if they:
- plan to or have already been moved to a digital phone line
- have concerns about reliability of their service
- have concerns about scams.
Further information:
AgeUK: Changes to Landline Telephones
Which?: Digital Voice and the Landline Phone Switch-off, What it Means for You
Monitoring
How do we know if telecare services are starting to be impacted?
Monitor existing services so any service reliability issues are identified and addressed.
Obtain reports on failed calls seen at the ARC:
- Understand what a 'normal' level of call failures looks like.
- Look for trends in failures – by equipment type, telecare protocol, and area.
- Look for high failure rates for individual service users (issues for individuals may be hidden if just looking at trends).
- Use the above information to identify service users or equipment types that are experiencing reliability issues and that need contingency measures to be put in place.
Collect and log information on service users that have moved to a digital telephone line.
- Collect information during regular maintenance/assessment visits.
- Ask when a service user calls the service (where appropriate and using suitable terminology).
- Use this information to assist you in resolving issues experienced by these service users and to potentially prioritise these service users in your digital telecare rollout planning.
Contingency
How do we minimise risk and impact?
Put arrangements in place to minimise the risk to service users before and after the move of their telephone line to digital. These could include:
- Help maximise the likelihood that telephone providers can identify which of their customers are telecare service users.
- Provide ARC telephone numbers to the TSA and telephone providers.
- Tell service users to inform their telephone provider they use telecare.
- Consider putting warning stickers for telephone engineers on telecare equipment and/or phone sockets in homes.
Help ensure that any communications from telephone providers sent to councils are passed to the relevant telecare service contacts. Telephone providers can send rollout information and dates to councils – however, they may use generic contact addresses.
Put contingency in place for service users whose telecare service is unreliable or inoperative following a telephone line migration. Example contingency measures include:
- Complete more regular telecare alarm tests / check-in calls.
- Maintain a stock of equipment known to operate reliably on digital lines for fast deployment to replace unreliable/inoperative equipment.
- Put arrangements in place with an organisation that can offer a digital telecare service – use this as an interim measure until you are able to offer a digital service yourself.
- Use alternative, non-telecare based, care arrangements.
Establish the potential impact of a mains power failure on service users with a digital telephone line and the contingency arrangements that need to put in place to respond if this happens.
Further information:
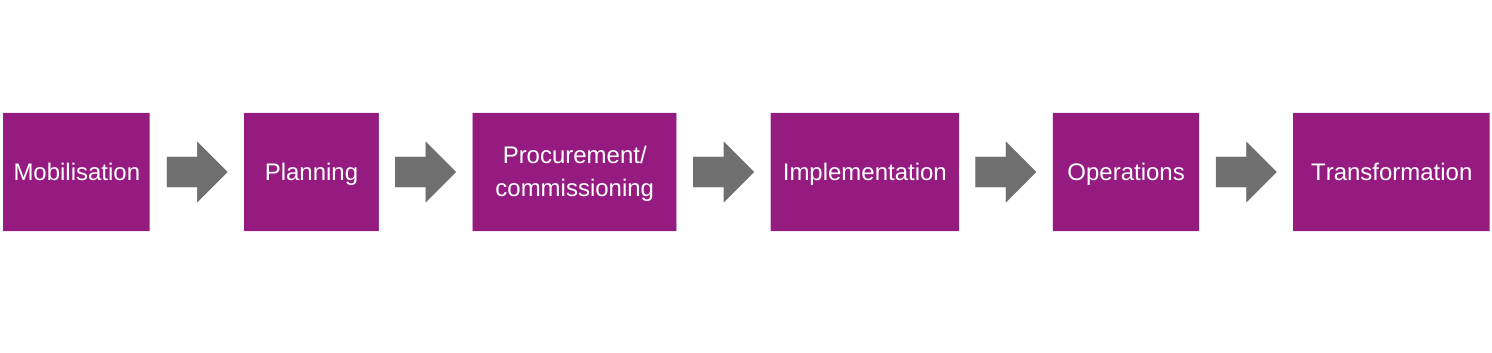
Future Services - Moving to Digital Telecare
Mobilisation
Forming a project team
Determine who needs to be involved in planning and implementing a digital telecare service. This is likely to include:
- social care and telecare teams
- commissioners
- IT and data protection teams
- finance and procurement colleagues
- service users
- equipment and service suppliers
- partner agencies and organisations.
Planning
What should a digital telecare service and technology solution look like?
Will the future telecare offering be a like-for-like move of existing service to digital or is it an opportunity to widen/transform the service offering?
Determine the service scope – What services can/should be offered to citizens? This is likely to consider:
- opportunities and benefits
- risks
- costs
- resource
- business case for change.
Determine the technology options that are available to deliver the digital services:
- Can/should the existing technology be retained, upgraded, or replaced?
- What is the impact of existing equipment on future choices? For example the potential need to replace existing peripheral devices if a different manufacturer's alarm device is used.
- What are the connectivity options and implications. Mobile and/or fixed broadband connectivity – their impact on connection reliability, cyber security risk, and costs.
Determine the potential costs and funding/charging options.
Further information:
Procurement/commissioning
How do we buy/commission a digital telecare service?
Determine how the new service/equipment will be sourced:
- Can/should you use your existing contract(s) for the new service, or is a new contract required?
How will the service be delivered:
- single / multiple supplier(s)
- commissioned service
- in-house
- combination of the above.
What procurement/commissioning routes are available?
What is the service/solution specification?
What changes to the existing arrangements are associated with the move to a digital service – for example:
- Who is responsible for monitoring and responding to the new/more regular information provided by digital equipment?
- Who is responsible for resolving issues with the technical solution/service – given the potential for greater reliance on a range of technology providers?
- How will the performance of the technology solution be monitored and reported on (a different approach is required for managing cloud-based, or ‘Software as a Service’, solutions compared to the traditional on-premises solutions)?
Further information:
Rethink Partners: LFA Digital Care Technology Procurement Planning Guide
NHS Shared Business Services: Technology Enabled Care Services 2 Framework
ESPO: Technology Enabled Care Products and Services
Procurement for Housing: Telecare, Telehealth & Associated Services Framework
Implementation
How do we implement digital telecare?
Establish the project tasks, timescales and resource requirements associated with the rollout of digital telecare.
What are the timescales and resource requirements? Including consideration of:
- The extent of the technology/service change – an extensive change to the service offering is likely to have a larger impact on resource, training and operational processes compared to a like-for-like shift of a service to digital.
- Availability of equipment from suppliers. Some suppliers are quoting very long lead times for digital equipment. This could limit the rate at which a rollout of digital services can be completed.
- Equipment installation resource. Replacement of in-home equipment is resource intensive, especially if new peripheral equipment is to be installed.
- Any upgrades to the wider infrastructure required to support the digital solution. This is especially relevant for the upgrades to the ARC and for grouped living systems, where upgrades to the wider IT infrastructure may be required – for example new Internet connectivity, firewalls, data cabling, etc.
- Training.
Establish if/how some service users should be prioritised in the rollout:
- Use the assessment of risk as detailed earlier in this checklist to support this process.
Develop a communications plan: Who needs to be informed, what needs to be communicated? How and when will this be done?
- service users
- staff
- suppliers
- other stakeholders.
What testing is required, and how and when will it be completed? This should include user testing and potentially cyber security testing.
Establish training requirements – installation/maintenance staff, assessor, social worker, call handler, and service user training may be required.
Establish if a period of dual running of analogue and digital telecare services is required. What is the impact of this on operational processes, staff and service users if two different systems are in use for a period of time?
Operations
What is the operational impact of digital telecare?
Establish if/how operational processes need to be updated to manage and deliver a digital telecare service. An extensive change to the service offering is likely to have a larger operational impact compared to a like-for-like shift of a service to digital:
Determine if the digital telecare system provides additional or more frequent data/alerts on service users or system health:
- Who will be responsible for monitoring this information? How frequently?
- What response is required to the information / alerts? Who is responsible for providing this response?
- What is the resource, skills and training impacts?
Is there a contractual/commissioning impact associated with the new/updated tasks or responsibilities?
Establish how issues with the performance or operation of the telecare service are resolved:
- Given that multiple suppliers could be involved in the delivery of the service - how do you determine which supplier is responsible for resolving an issue? (for example, ARC provider, alarm device provider(s), internet provider(s), internal IT teams, etc).
- How/when are suppliers contacted in the event of an issue? Are they available outside normal working hours?
- Is there a requirement for IT skills/support to assist with triaging and resolving service issues?
Transformation
How to make best use of digital technology and where next?
Determine how digital technology can be used further to improve / transform services and service delivery. This could include:
- Potential for offering proactive / predictive / personalised services.
- Better use of smart consumer technology and Internet of Things (IoT).
- Better use of data and analytics.
- Supporting closer integration with other health, care, and housing providers.
How and when can/should these services be rolled out.
Further information:
Department for Health & Social Care: A Plan for Digital Health & Social Care
Digital Health & Care Scotland: Digital Health & Care Strategy
LGA case studies: Suffolk Council and Gateshead Council
Digital Office for Scottish Local Government case studies
Housing LIN: Technology for our Ageing Population